Fire is the most dangerous thing that we can face in our lives. That’s why fire safety regulations are so important to keep people safe in a building. These safety regulations ensure that your building has working fire alarms, strong fire doors, clear escape routes, and regular safety checks.
In London, these rules are regularly updated and have changed since 2022. These updated regulations ensure that building owners, landlords, and managers know how to keep people safe. Now the question is how you can know about fire safety legal requirements.
In this blog, we discuss the Fire Safety Regulations Act. Also, we explain clearly what fire safety regulations are all about.
What are the key changes in the latest Fire Safety Regulations Act?

To keep people safe, the Fire Safety Regulations Act is being updated. Whatever the size of the building, fire risk checks must be recorded. Take a look at that table to understand the key changes in UK fire safety regulations:
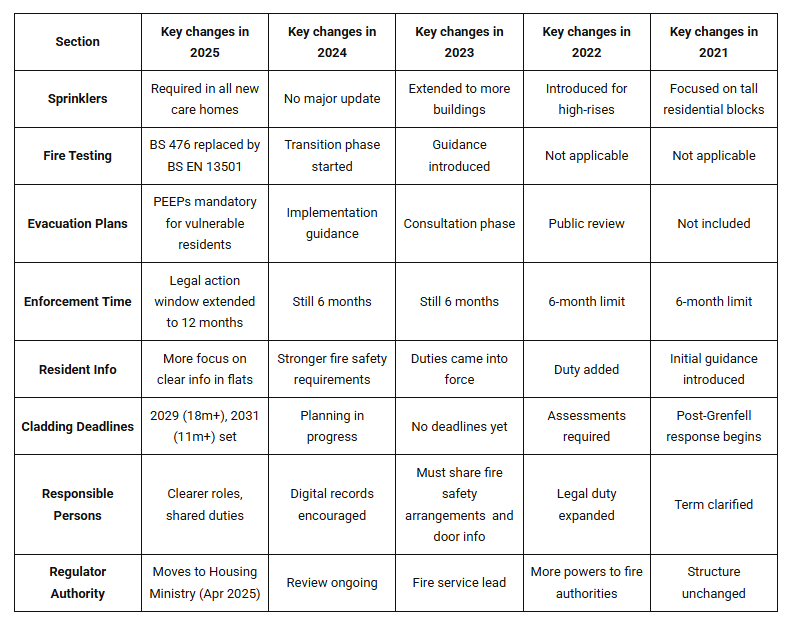
Here, we break down each year’s fire safety England regulations. To help you learn how these regulations are kept updated and how they improve fire safety.
Key Amendments to the Fire Safety Act 2021
The Fire Safety Act 2021 is a new law made after the Grenfell Tower fire. After that incident, fire safety rules were updated.
Key changes:
![]() The scope of fire risk assessments was formally expanded to include external walls, balconies, and flat entrance doors.
The scope of fire risk assessments was formally expanded to include external walls, balconies, and flat entrance doors.![]() Building owners, landlords, and managing agents were formally identified as Responsible Persons under the law.
Building owners, landlords, and managing agents were formally identified as Responsible Persons under the law.![]() The Act confirmed that the Regulatory Reform Order 2005 applies to a building’s structure, cladding, and other external features.
The Act confirmed that the Regulatory Reform Order 2005 applies to a building’s structure, cladding, and other external features.![]() This Act formed the legal foundation for later measures, including the Fire Safety Act 2022 and the Fire Safety Regulations 2022.
This Act formed the legal foundation for later measures, including the Fire Safety Act 2022 and the Fire Safety Regulations 2022.![]() Initial statutory guidance was issued to support the communication of fire safety information to residents.
Initial statutory guidance was issued to support the communication of fire safety information to residents.
How the Fire Safety Act 2022 has transformed compliance requirements
All Fire Safety Regulation 2022 (from Jan 2023)
![]() Applies to multi-occupied residential buildings and high-rise residential buildings (over 11m).
Applies to multi-occupied residential buildings and high-rise residential buildings (over 11m).![]() Regulation 7 sets out additional legal duties for persons responsible for high-rise residential buildings.
Regulation 7 sets out additional legal duties for persons responsible for high-rise residential buildings.![]() Responsible Persons (owners/managers) must provide detailed floor/building plans for fire safety risk.
Responsible Persons (owners/managers) must provide detailed floor/building plans for fire safety risk.![]() Must supply info on external wall systems to local fire and rescue services (high-rise only).
Must supply info on external wall systems to local fire and rescue services (high-rise only).![]() Require a secure premises information box with fire plans accessible to fire & rescue.
Require a secure premises information box with fire plans accessible to fire & rescue.![]() Monthly checks of firefighter lifts, evacuation lifts, and fire equipment, with fault reporting.
Monthly checks of firefighter lifts, evacuation lifts, and fire equipment, with fault reporting.![]() Firefighter wayfinding signage is mandatory in high-rise buildings to assist the fire brigade during emergencies.
Firefighter wayfinding signage is mandatory in high-rise buildings to assist the fire brigade during emergencies.![]() Importance of Fire door checks: communal doors quarterly, flat entrance doors annually, and self-closing devices maintained.
Importance of Fire door checks: communal doors quarterly, flat entrance doors annually, and self-closing devices maintained.![]() Residents must receive clear fire safety instructions and info about fire doors (keep closed, report faults).
Residents must receive clear fire safety instructions and info about fire doors (keep closed, report faults).
Act 2022 Section 156 of the Building Safety (From October 2023)
![]() Strengthens responsibilities for all Responsible Persons (not high-rise).
Strengthens responsibilities for all Responsible Persons (not high-rise).![]() Must fully record their fire safety risk assessment findings.
Must fully record their fire safety risk assessment findings.![]() Document fire safety management arrangements.
Document fire safety management arrangements.![]() Record the identity and competence of fire risk assessors.
Record the identity and competence of fire risk assessors.![]() Maintain and share the UK contact address for notices.
Maintain and share the UK contact address for notices.![]() Coordinate and share responsibilities with other Responsible Persons in the same building.
Coordinate and share responsibilities with other Responsible Persons in the same building.![]() Hand over full fire safety responsibilities info when a change.
Hand over full fire safety responsibilities info when a change.![]() Provide residents with clear, relevant fire safety information.
Provide residents with clear, relevant fire safety information.![]() Increased fines for breaches (some unlimited).
Increased fines for breaches (some unlimited).![]() Fire Safety guidance has a stronger legal weight in court.
Fire Safety guidance has a stronger legal weight in court.
Understanding the Fire Safety Regulations 2023/2024 amendments
In these years, new regulations require those responsible for the safety of buildings to fulfil legal duties.
Key changes in 2023
![]() Fire door checks became a legal requirement in buildings over 11 meters.
Fire door checks became a legal requirement in buildings over 11 meters.![]() Residents had to receive clear fire safety instructions, including evacuation details.
Residents had to receive clear fire safety instructions, including evacuation details.![]() Fire risk assessments were required to cover external walls, balconies, and flat entrance doors.
Fire risk assessments were required to cover external walls, balconies, and flat entrance doors.![]() Sprinkler requirements were expanded to include more types of residential buildings.
Sprinkler requirements were expanded to include more types of residential buildings.![]() A new fire testing standard (BS EN 13501) began replacing the previous BS 476 fire.
A new fire testing standard (BS EN 13501) began replacing the previous BS 476 fire.
Personal Emergency Evacuation Plans (PEEPs) entered the guidance stage for buildings housing vulnerable residents.
Then, the fire safety regulations 2024 add new rules to keep people safe from fire. These rules also ensure that building owners and managers know how they easily save people.
Key changes in 2024
![]() Stronger expectations around the sharing of fire safety information with residents.
Stronger expectations around the sharing of fire safety information with residents.![]() Responsible persons were encouraged to maintain a digital recording and sharing of fire.
Responsible persons were encouraged to maintain a digital recording and sharing of fire.![]() Further movement towards full adoption of BS EN 13501 for fire testing.
Further movement towards full adoption of BS EN 13501 for fire testing.![]() Implementation guidance for PEEPs was published
Implementation guidance for PEEPs was published![]() The government began transitioning regulatory responsibility to the Department for Levelling Up, Housing, and Communities.
The government began transitioning regulatory responsibility to the Department for Levelling Up, Housing, and Communities.
Timeline for implementing new fire safety legislation changes
2022
2023
2024



2025
Who Is Responsible for Fire Safety Under the Current Legislation?

If you’re wondering, who is responsible for fire safety legislation in England? So, the answer depends on the types of property and buildings. According to UK regulations, the “Responsible Person” role is based on property type, such as:
![]() In workplaces: usually the employer.
In workplaces: usually the employer.![]() In commercial buildings: the owner, occupier, or managing agent.
In commercial buildings: the owner, occupier, or managing agent.![]() In rented homes: the landlord, particularly responsible for communal areas.
In rented homes: the landlord, particularly responsible for communal areas.![]() In shared buildings: there may be multiple responsible persons.
In shared buildings: there may be multiple responsible persons.
Legal Duties of the “Responsible Person” in Commercial Properties
If you’re an owner or manager of a business, then you must understand your duties. In London, business owners or managers need to follow commercial property fire safety regulations. Some rules are different from those that cover homes, like the ones under fire safety for landlords. Check this, key responsibilities of the responsible person:
![]() Completing a fire risk assessment and reviewing it regularly, or conducting quarterly checks of all fire assessments
Completing a fire risk assessment and reviewing it regularly, or conducting quarterly checks of all fire assessments![]() Identifying people at risk, such as employees or visitors.
Identifying people at risk, such as employees or visitors.![]() Installing fire alarms and smoke detectors.
Installing fire alarms and smoke detectors.![]() Providing firefighting equipment, like fire extinguishers.
Providing firefighting equipment, like fire extinguishers.![]() Ensuring emergency lighting is working in escape routes.
Ensuring emergency lighting is working in escape routes.![]() Keeping fire exits clear and unlocked.
Keeping fire exits clear and unlocked.![]() Creating an emergency evacuation plan.
Creating an emergency evacuation plan.![]() Displaying fire safety signs clearly around the building.
Displaying fire safety signs clearly around the building.![]() Providing fire safety training for all staff.
Providing fire safety training for all staff.![]() Checking electrical appliances and wiring regularly.
Checking electrical appliances and wiring regularly.![]() Storing flammable materials safely.
Storing flammable materials safely.![]() Arranging regular fire drills and recording the results.
Arranging regular fire drills and recording the results.![]() Cooperating with the fire and rescue service during assessments and incidents.
Cooperating with the fire and rescue service during assessments and incidents.![]() Ensuring fire safety measures are suitable for residential buildings with stores over 11 meters, if applicable.
Ensuring fire safety measures are suitable for residential buildings with stores over 11 meters, if applicable.![]() Making sure all systems and protocols are appropriate for the building’s fire risks and structure.
Making sure all systems and protocols are appropriate for the building’s fire risks and structure.
Landlord Responsibilities for Fire Safety in Residential Buildings
In London, landlords need to follow fire safety rules. This helps keep people safe and protects the property. These rules are called fire safety regulations for landlords. They also apply to shared homes like HMOs. If you’re a landlord, these are the key fire safety steps you need to follow:
![]() Check the home for fire risks and review it regularly.
Check the home for fire risks and review it regularly.![]() Follow all domestic fire regulations for rented homes.
Follow all domestic fire regulations for rented homes.![]() Put smoke alarms on each floor and test them often.
Put smoke alarms on each floor and test them often.![]() Add carbon monoxide alarms where needed.
Add carbon monoxide alarms where needed.![]() Follow fire rags for HMOs in shared or multi-tenant homes.
Follow fire rags for HMOs in shared or multi-tenant homes.![]() Keep hallways, stairs, and exits clear at all times.
Keep hallways, stairs, and exits clear at all times.![]() Use fire-safe furniture and materials in the property.
Use fire-safe furniture and materials in the property.![]() Make sure emergency lights work in dark escape routes.
Make sure emergency lights work in dark escape routes.![]() Checks of all fire doors that shut by themselves and aren’t damaged.
Checks of all fire doors that shut by themselves and aren’t damaged.![]() Provide fire blankets or extinguishers in shared kitchens if required.
Provide fire blankets or extinguishers in shared kitchens if required.![]() Work with local fire and rescue during visits or inspections.
Work with local fire and rescue during visits or inspections.![]() Put up simple fire escape plans and emergency contact info.
Put up simple fire escape plans and emergency contact info.![]() Take extra care in residential buildings with storeys over 11 meters.
Take extra care in residential buildings with storeys over 11 meters.![]() Make sure all fire safety steps fit your building and the people living in it.
Make sure all fire safety steps fit your building and the people living in it.
Consequences of Non-Compliance with Fire Safety Regulations
If you’re a landlord or business owner, and you don’t follow fire safety rules. These are the results you face:Notices from the fire authority.
![]() Orders stopping the use of unsafe parts of a building.
Orders stopping the use of unsafe parts of a building.![]() Fines that cost thousands of pounds.
Fines that cost thousands of pounds.![]() Criminal charges in major cases.
Criminal charges in major cases.![]() Prison for extreme failures.
Prison for extreme failures.![]() Legal action if someone gets hurt or dies.
Legal action if someone gets hurt or dies.![]() Higher insurance costs or no coverage.
Higher insurance costs or no coverage.![]() Damage to business or personal reputation.
Damage to business or personal reputation.![]() Building closure until safety is restored.
Building closure until safety is restored.![]() Loss of trust from tenants or the public.
Loss of trust from tenants or the public.
Fire safety isn’t a proper work, it’s a legal duty. Follow all these rules and safe people and their property safe.
What Are the Essential Fire Safety Equipment Requirements?

Fire safety equipment plays a vital role in protecting people and their property from fire. In any type of property, you need to install this equipment. Let’s dive into this.
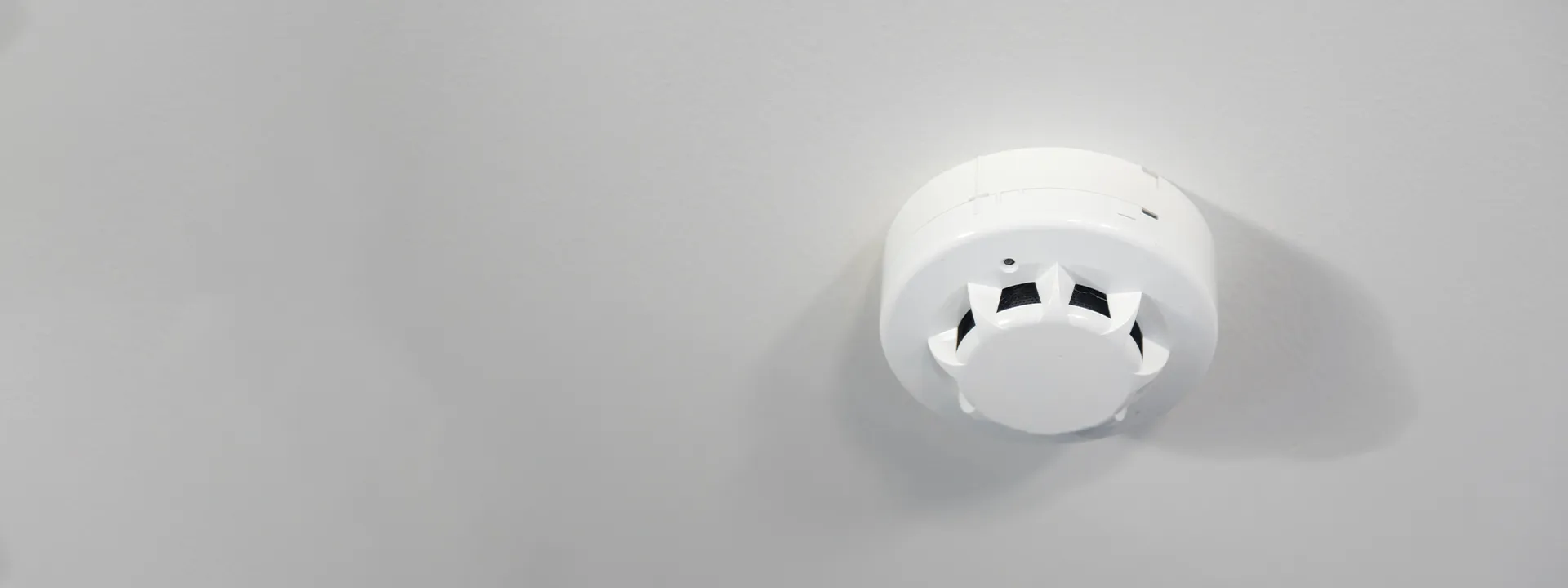
Fire Alarm Regulations and Testing Frequencies
When a fire starts, the fire alarm alerts everyone. So, people can leave the place quickly. That’s why everyone must know about regulations. Let’s explore this:
![]() Types of Alarms: Domestic homes use smoke or heat alarms. Commercial and HMO properties need automatic systems with sounders and manual call points.
Types of Alarms: Domestic homes use smoke or heat alarms. Commercial and HMO properties need automatic systems with sounders and manual call points.![]() Testing Frequency: Alarms should be tested weekly by pressing the test button. Larger systems require monthly checks by trained personnel.
Testing Frequency: Alarms should be tested weekly by pressing the test button. Larger systems require monthly checks by trained personnel.![]() Servicing: Fire alarm systems must be professionally serviced every 6 months under BS 5839 standards.
Servicing: Fire alarm systems must be professionally serviced every 6 months under BS 5839 standards.![]() Battery Checks: Battery-powered units batteries are replaced annually, or sooner if the low battery warning sounds.
Battery Checks: Battery-powered units batteries are replaced annually, or sooner if the low battery warning sounds.![]() System Zones: For large buildings, zones must be clearly marked to identify where the fire is detected.
System Zones: For large buildings, zones must be clearly marked to identify where the fire is detected.![]() Log Book: Keep a fire log book with all testing dates, results, faults found, and actions taken.
Log Book: Keep a fire log book with all testing dates, results, faults found, and actions taken.
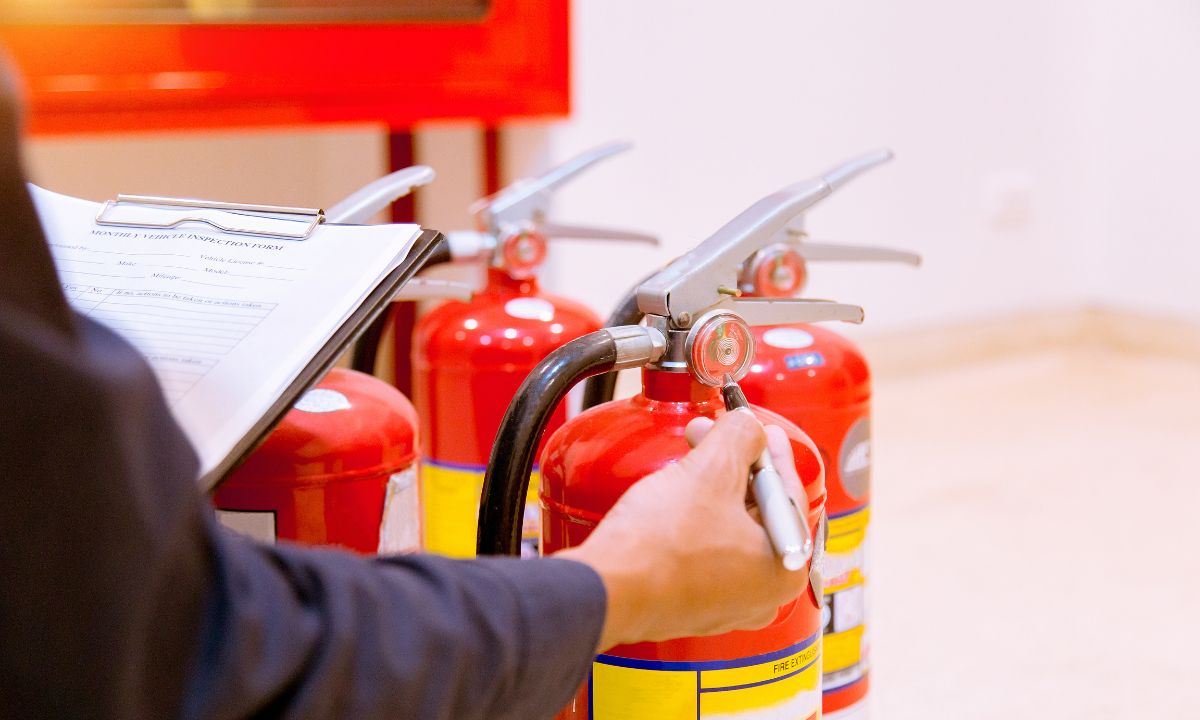
Fire Extinguisher Regs and Maintenance Schedules
A fire extinguisher helps stop small fires before they spread. If you can use it in the right way, then it works fast and can stop damage or danger. Let’s learn about that:
![]() Types of Extinguishers: Water, CO2, foam, powder, and wet chemical – each for different fire types (A, B, C, D, electrical, or cooking fires).
Types of Extinguishers: Water, CO2, foam, powder, and wet chemical – each for different fire types (A, B, C, D, electrical, or cooking fires).![]() Placement: Must be easily accessible and located near exits or high-risk areas like kitchens or workshops.
Placement: Must be easily accessible and located near exits or high-risk areas like kitchens or workshops.![]() Number Required: Based on the size and risk level of the building. A typical office needs at least two extinguishers per floor.
Number Required: Based on the size and risk level of the building. A typical office needs at least two extinguishers per floor.![]() Annual Servicing: A qualified engineer must inspect and service every extinguisher at least once a year.
Annual Servicing: A qualified engineer must inspect and service every extinguisher at least once a year.![]() Extended Servicing: Every 5 years (or 10 for CO2), full discharge and pressure testing is required.
Extended Servicing: Every 5 years (or 10 for CO2), full discharge and pressure testing is required.![]() Visual Checks: Monthly inspections should be done to check pressure, tamper seals, and general condition.
Visual Checks: Monthly inspections should be done to check pressure, tamper seals, and general condition.
Fire Safety Doors Regulations and Compliance Standards
Fire safety doors stop fire and smoke from moving around inside a building. It keeps people safe, and gives them time to get out. Let’s see how it works:
![]() What Are Fire Doors?: Specially designed doors made to resist fire and smoke, rated FD30 or FD60 (30- or 60-minutes protection).
What Are Fire Doors?: Specially designed doors made to resist fire and smoke, rated FD30 or FD60 (30- or 60-minutes protection).![]() Where Required: In HMOs, commercial buildings, and between garages and homes. Also, on stairwells and escape routes.
Where Required: In HMOs, commercial buildings, and between garages and homes. Also, on stairwells and escape routes.![]() Regulations: Must meet BS 476 or BS EN 1634 standards for fire resistance and be correctly fitted with intumescent seals.
Regulations: Must meet BS 476 or BS EN 1634 standards for fire resistance and be correctly fitted with intumescent seals.![]() Maintenance: Check regularly that they close fully, the seals are intact, and the hinges and latches work correctly.
Maintenance: Check regularly that they close fully, the seals are intact, and the hinges and latches work correctly.![]() Signage: Fire doors must be marked with “Fire Door – Keep Shut” signs on both sides unless they are held open by approved devices.
Signage: Fire doors must be marked with “Fire Door – Keep Shut” signs on both sides unless they are held open by approved devices.![]() Certification: Fire doors should have a manufacturer’s label or plug showing they’ve been tested and approved.
Certification: Fire doors should have a manufacturer’s label or plug showing they’ve been tested and approved.
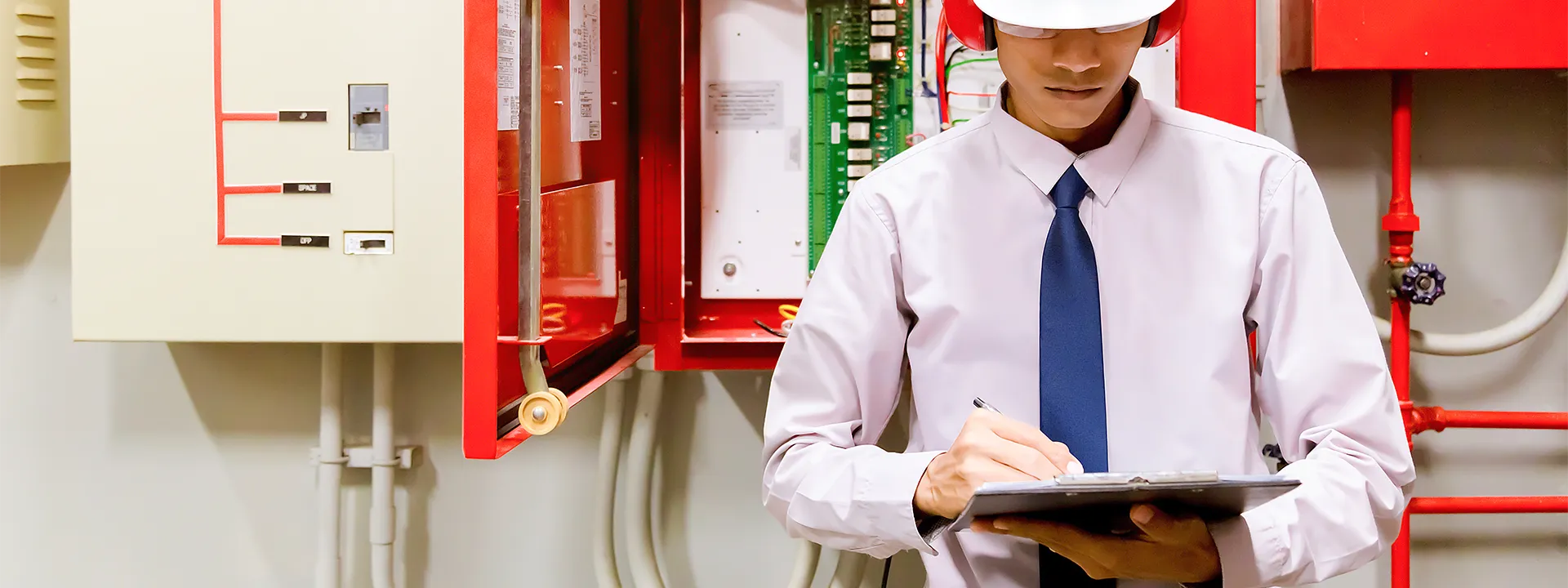
What Does a Legally Compliant Fire Risk Assessment Include?

A fire risk assessment is a way to check your building for fire danger. Because the goal is to keep everyone safe. A legally compliant fire risk assessment helps you to fix problems and ensure that your taunts or building are safe for people.
Make sure the assessment looks at:
![]() Fire hazards – things like flammable materials, faulty wiring, overloaded sockets, or anything that could cause or fuel a fire
Fire hazards – things like flammable materials, faulty wiring, overloaded sockets, or anything that could cause or fuel a fire![]() People at risk – staff, visitors, residents, and anyone who may need help to escape (like children, elderly people, or those with mobility issues)
People at risk – staff, visitors, residents, and anyone who may need help to escape (like children, elderly people, or those with mobility issues)![]() Fire risks and solutions – spot dangers and decide how to remove or reduce them
Fire risks and solutions – spot dangers and decide how to remove or reduce them![]() Fire safety equipment – check that alarms, extinguishers, emergency lights, and fire doors are in good condition and working properly
Fire safety equipment – check that alarms, extinguishers, emergency lights, and fire doors are in good condition and working properly![]() Emergency plan – make sure there’s a clear evacuation plan with safe routes and meeting points
Emergency plan – make sure there’s a clear evacuation plan with safe routes and meeting points![]() Training – staff need to know what to do if there’s a fire, including regular fire drills
Training – staff need to know what to do if there’s a fire, including regular fire drills![]() Signs and instructions – make sure exits and fire equipment are clearly marked with the right signs
Signs and instructions – make sure exits and fire equipment are clearly marked with the right signs![]() Storage – flammable materials must be stored safely and handled with care
Storage – flammable materials must be stored safely and handled with care![]() Record keeping – write down what you found, what actions were taken, and who is responsible
Record keeping – write down what you found, what actions were taken, and who is responsible![]() Regular reviews – check the fire risk assessment regularly, especially if anything changes in the building
Regular reviews – check the fire risk assessment regularly, especially if anything changes in the building
If you have a business and a lot of employees, then the fire risk assessment must be noted. For shared buildings or flats, have extra rules under the Fire Safety Regulations 2022, like checking fire doors.
Fire Risk Assessment Regulations and Documentation Requirements
In London, fire safety rules apply to all types of buildings, such as offices, shops, schools, care homes, and shared parts of flats. These Fire risk assessment regulations come from a law called the Regulatory Reform Order or Fire Safety Order (FSO) 2005.
What documents do you need?
![]() A written fire risk assessment.
A written fire risk assessment.![]() Notes about fire safety measures you’ve taken.
Notes about fire safety measures you’ve taken.![]() Proof that staff have had fire safety training.
Proof that staff have had fire safety training.![]() Maintenance records for fire alarms, emergency lights, and extinguishers.
Maintenance records for fire alarms, emergency lights, and extinguishers.![]() A clear, easy-to-find emergency plan.
A clear, easy-to-find emergency plan.
How Often Should Fire Risk Assessments Be Updated?
You should update your fire risk assessment regularly. Here we create a list especially when your need to be update it:
![]() There are changes to the building structure or layout.
There are changes to the building structure or layout.![]() The use of the premises changes.
The use of the premises changes.![]() New equipment or machinery is introduced.
New equipment or machinery is introduced.![]() There’s been a fire or near-miss incident.
There’s been a fire or near-miss incident.![]() A significant number of staff changes.
A significant number of staff changes.
As per the general rule, it’s best to review your fire risk assessment at least once a year.
Who Can Conduct a Valid Fire Risk Assessment?
Fire risk assessment is an essential part of any building. That’s why it needs to be done by someone who knows how to check for fire dangers and understands fire safety rules. Here’s who can conduct a legally compliant fire risk assessment:
![]() The responsible person: The business owner, employer, landlord, or building manager.
The responsible person: The business owner, employer, landlord, or building manager.![]() An employee or staff member: If they have proper fire safety training and understand the specific risks of the premises safe from fire.
An employee or staff member: If they have proper fire safety training and understand the specific risks of the premises safe from fire.![]() A professional fire risk assessor: Someone qualified and experienced in carrying out fire risk assessments for different types of buildings.
A professional fire risk assessor: Someone qualified and experienced in carrying out fire risk assessments for different types of buildings.![]() A fire safety consultant or company: Especially useful for large, complex, or high-risk buildings.
A fire safety consultant or company: Especially useful for large, complex, or high-risk buildings.![]() Third-party accredited assessors: Professionals who are certified by recognized bodies (like BAFE or the Institute of Fire Engineers)
Third-party accredited assessors: Professionals who are certified by recognized bodies (like BAFE or the Institute of Fire Engineers)
How Should Businesses Create a Compliant Fire Safety Emergency Response Plan?

Each and every business needs to have a fire safety emergency plan. This plan helps your business follow the law, keep everyone safe, and save your pounds. But your plan must follow the local fire safety law. Ensure that the plan is clear, easy to read and easy to follow. Take a look on this list:
![]() Identify fire risks and hazards in the building through a proper fire risk assessment.
Identify fire risks and hazards in the building through a proper fire risk assessment.![]() Include clear emergency evacuation routes and fire exit signage in the plan.
Include clear emergency evacuation routes and fire exit signage in the plan.![]() Assign roles for staff like fire wardens and first aid responders.
Assign roles for staff like fire wardens and first aid responders.![]() Add emergency contact numbers, alarm system details, and fire equipment locations.
Add emergency contact numbers, alarm system details, and fire equipment locations.![]() Review and update the plan regularly to stay compliant with local fire codes.
Review and update the plan regularly to stay compliant with local fire codes.![]() Ensure the plan includes procedures for alerting emergency services.
Ensure the plan includes procedures for alerting emergency services.
Fire Safety Evacuation Procedures for Different Building Types
All buildings are different. That’s why a small office around 300 square meters needs a different plan than a big warehouse over 2,000 square meters. Here is the list:
![]() Office buildings need marked exits, regular drills, and PA system alerts.
Office buildings need marked exits, regular drills, and PA system alerts.![]() High-rise buildings require stairwell evacuation procedures and smoke control systems.
High-rise buildings require stairwell evacuation procedures and smoke control systems.![]() Factories should consider flammable materials and large floor areas.
Factories should consider flammable materials and large floor areas.![]() Schools need staff to guide children safely and perform headcounts.
Schools need staff to guide children safely and perform headcounts.![]() Hospitals must include evacuation chairs and patient movement plans.
Hospitals must include evacuation chairs and patient movement plans.![]() All types must follow fire evacuation regulations and occupant load rules.
All types must follow fire evacuation regulations and occupant load rules.
Fire Code Emergency Lighting Requirements If the electricity goes out during a fire, that time emergency lighting becomes a lifesaver. Here’s why:
![]() Install lighting along corridors, stairs, and fire exits.
Install lighting along corridors, stairs, and fire exits.![]() Use signage with backup power to stay visible during blackouts.
Use signage with backup power to stay visible during blackouts.![]() Follow NFPA 101 Life Safety Code or local building codes.
Follow NFPA 101 Life Safety Code or local building codes.![]() Test emergency lights monthly and keep maintenance logs.
Test emergency lights monthly and keep maintenance logs.![]() Lighting must last for at least 90 minutes during an outage.
Lighting must last for at least 90 minutes during an outage.![]() Ensure visibility of exit signs from every point in a hallway.
Ensure visibility of exit signs from every point in a hallway.
Staff Training Requirements Under Current Legislation
Fire safety training is a must for all employees. Here we create a list, take a look:
![]() Teach staff how to use fire extinguishers and locate alarms.
Teach staff how to use fire extinguishers and locate alarms.![]() Explain evacuation routes and safe assembly points.
Explain evacuation routes and safe assembly points.![]() Conduct fire drills at least once or twice a year.
Conduct fire drills at least once or twice a year.![]() Train new employees during onboarding and repeat as needed.
Train new employees during onboarding and repeat as needed.![]() Assign roles such as fire wardens and ensure they are trained.
Assign roles such as fire wardens and ensure they are trained.![]() Follow national laws like the Regulatory Reform Order 2005.
Follow national laws like the Regulatory Reform Order 2005.
What fire safety regulations apply to specific property types?

Fire safety rules depend on the kinds of property you have. If you have a commercial building, an HMO, or a private home, school, or coffee shop, whatever it is. To stay compliant, you must know the fire safety regulations.
In this section, we talk about key fire safety rules for each type of property. We break down these with checklists, definitions, and terms like fire risk assessment, fire extinguisher placement, smoke alarms, and fire escape routes, everything.
Commercial property fire safety regulations and compliance checklist
Here, we talk about Commercial property fire safety regulations. Commercial property means all types of shops, offices, warehouses, and factories.How can youprotect your visitors, staff, and the property? Take a look at this checklist:
![]() Fire Risk Assessment: A legal requirement. Identify hazards, people at risk, and ways to reduce fire risks. Must be reviewed regularly.
Fire Risk Assessment: A legal requirement. Identify hazards, people at risk, and ways to reduce fire risks. Must be reviewed regularly.![]() Escape Routes: Clear, well-marked fire exits must be available. Emergency lighting should guide people in low visibility.
Escape Routes: Clear, well-marked fire exits must be available. Emergency lighting should guide people in low visibility.![]() Check your Fire Alarms: You must install and maintain a working fire alarm system. Test weekly and service regularly.
Check your Fire Alarms: You must install and maintain a working fire alarm system. Test weekly and service regularly.![]() Fire Extinguishers: Choose the right type (water, CO2, foam, etc.) for different fire classes. Keep them in easy-to-reach spots.
Fire Extinguishers: Choose the right type (water, CO2, foam, etc.) for different fire classes. Keep them in easy-to-reach spots.![]() Staff Training: Employees should know what to do in a fire, how to use fire equipment, and how to evacuate safely.
Staff Training: Employees should know what to do in a fire, how to use fire equipment, and how to evacuate safely.![]() Fire Safety Signs: Install signs showing fire exits, extinguisher locations, and fire action notices. They must be visible and up to code.
Fire Safety Signs: Install signs showing fire exits, extinguisher locations, and fire action notices. They must be visible and up to code.
For non-domestic premises, you must follow the above rules. These regulations help you to reduce risk and save your pounds. And you stay compliant.
Fire regs for HMO(Houses in Multiple Occupation) explained
If you manage, own, or live in an HMO, then you have to follow some extra fire safety rules. HMOs fall under multi-occupied residential properties. It means a lot of people under one roof. They shared rooms like kitchens, hallways, and washrooms etc. To keep everyone safe, you need a clean fire safety plan.
For HMOs or multi-occupied residential buildings, we create a checklist here:
![]() You need a proper fire risk assessment that covers the whole building.
You need a proper fire risk assessment that covers the whole building.![]() Install fire doors in key rooms like kitchens and bedrooms. These slow the spread of fire and smoke.
Install fire doors in key rooms like kitchens and bedrooms. These slow the spread of fire and smoke.![]() Keep clear, marked fire escape routes.
Keep clear, marked fire escape routes.![]() Use fire doors that close on their own.
Use fire doors that close on their own.![]() Place fire extinguishers or fire blankets in key areas like kitchens.
Place fire extinguishers or fire blankets in key areas like kitchens.![]() Ensure emergency lighting in hallways and staircases.
Ensure emergency lighting in hallways and staircases.![]() Keep fire escape routes free from obstacles.
Keep fire escape routes free from obstacles.![]() Regularly test smoke alarms and fire equipment.
Regularly test smoke alarms and fire equipment.![]() Check fire doors regularly to make sure they close properly.
Check fire doors regularly to make sure they close properly.![]() Display clear fire safety signs throughout the building.
Display clear fire safety signs throughout the building.![]() Inform tenants about fire safety procedures and escape plans.
Inform tenants about fire safety procedures and escape plans.![]() Inspect electrical wiring and appliances to avoid fire risks.
Inspect electrical wiring and appliances to avoid fire risks.![]() Do not allow smoking inside the property.
Do not allow smoking inside the property.![]() Store flammable materials safely away from heat sources.
Store flammable materials safely away from heat sources.![]() Display emergency contact numbers clearly for quick access.
Display emergency contact numbers clearly for quick access.
Domestic fire regulations for residential properties
In domestic premises, such as a standard home, fire safety measures focus on early detection. On the other hand, sets of domestic premises need fire-safe communal areas. These rules apply to homeowners, tenants, and landlords of single-family homes.
Here is the checklist:
![]() Install one smoke alarm per floor and test monthly.
Install one smoke alarm per floor and test monthly.![]() Use carbon monoxide alarms with solid fuel appliances.
Use carbon monoxide alarms with solid fuel appliances.![]() Plan and practice a fire escape route regularly.
Plan and practice a fire escape route regularly.![]() Don’t overload sockets, hire a qualified electrician for checks.
Don’t overload sockets, hire a qualified electrician for checks.![]() Never leave cooking unattended, keep flammable items away from heat.
Never leave cooking unattended, keep flammable items away from heat.![]() Place fire blankets or extinguishers in kitchen areas.
Place fire blankets or extinguishers in kitchen areas.![]() Keep escape routes clear and unblocked at all times.
Keep escape routes clear and unblocked at all times.![]() Use fire doors that close automatically.
Use fire doors that close automatically.![]() Install emergency lighting in halls and stairways.
Install emergency lighting in halls and stairways.![]() Test smoke alarms and all fire equipment regularly.
Test smoke alarms and all fire equipment regularly.![]() Put up clear fire safety signs in key locations.
Put up clear fire safety signs in key locations.![]() Inform tenants about fire safety rules and escape plans.
Inform tenants about fire safety rules and escape plans.![]() Display emergency contact numbers in visible areas.
Display emergency contact numbers in visible areas.![]() Keep a fire safety logbook for checks and maintenance records.
Keep a fire safety logbook for checks and maintenance records.![]() Ensure windows and exits are not blocked or locked.
Ensure windows and exits are not blocked or locked.![]() Teach everyone to Stop, Drop, and Roll in case clothes catch fire.
Teach everyone to Stop, Drop, and Roll in case clothes catch fire.
Now that you’ve read this blog, you have a good understanding of the fire safety rules from 2021 to 2025. These rules are updated regularly to keep your property safe. To learn more and stay compliant, visit alllandlordcertificates.co.uk. We make fire risk checks and certificates simple and hassle-free.
Keep your property safe, skip the fines, and get your fire safety certificate with us today.












